Embracing Dietary Changes for Diabetes Management
The Crucial Role of Diet in Diabetes
Living with diabetes means more than just monitoring blood sugar levels; it involves a holistic approach to lifestyle, with diet playing a starring role. The foods we eat can have a profound impact on blood sugar control and overall health. This guide is designed to unveil the potential of diet in managing diabetes, offering delicious and nutritious options that align with your health goals.
Beyond Blood Sugar Control: A Holistic Approach
While the primary focus is on foods that aid in blood sugar regulation, it’s equally important to consider overall well-being. The foods I’ll introduce are not just beneficial for managing diabetes but also contribute to heart health, weight management, and general vitality. As someone who’s passionate about nutritious living, I understand the importance of a diet that supports all aspects of health.
Empowering Through Education and Choice
Before we dive into the list, it’s crucial to understand that managing diabetes through diet isn’t about stringent rules but about making informed choices. This guide is more than just a list of foods; it’s a tool to empower you with knowledge and options. Whether you’re newly diagnosed, looking to revamp your diet, or seeking to maintain healthy blood sugar levels, these foods can be a valuable addition to your dietary arsenal.

13. Chia Seeds: The Tiny Powerhouse
Chia seeds, with their Glycemic Index (G.I) of just 30, fall comfortably in the low GI category, making them ideal for maintaining stable blood sugar levels. Foods with a GI of 55 or less, like chia seeds, release glucose slowly into the bloodstream, preventing the rapid spikes associated with high GI foods (those with a GI above 70). This slow release is crucial for effective diabetes management.
Nutritional Benefits: Fiber, Omega-3s, and More
Packed with dietary fiber, omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, magnesium, and calcium, chia seeds are a nutritional powerhouse. The soluble fiber in chia seeds is particularly beneficial, as it slows digestion and glucose absorption, aiding in blood sugar regulation. Omega-3 fatty acids, on the other hand, improve insulin sensitivity.
Incorporating Chia Seeds in Your Diet
Chia seeds are incredibly versatile and can be easily added to your diet. They can be sprinkled on salads, blended into smoothies, or used as a thickener in soups and sauces. These simple yet effective methods make chia seeds a practical choice for managing diabetes.
12. Avocado: The Creamy Superfood
Avocados are a treasure trove of nutrients, boasting about 10 grams of fiber per fruit and 15 grams of monounsaturated fats. These elements are essential for heart health and blood sugar regulation. A study in the ‘Nutrition Journal’ highlighted that regular avocado consumption could reduce the risk of metabolic syndrome by up to 50%. Since metabolic syndrome is closely linked to diabetes, avocados are a valuable addition to a diabetic diet.

Weight Management and Diabetes
The high fiber content in avocados not only aids in blood sugar control but also plays a role in maintaining a healthy weight. Weight management is a key factor in diabetes management, making avocados an excellent choice for those looking to balance their diet.
Delicious Ways to Enjoy Avocado
Avocados can be added to salads, used in sandwiches, or spread on whole-grain toast. Their creamy texture and rich flavor make them a delicious and nutritious option for anyone looking to enhance their diet.

11. Shirataki Noodles: The Zero-Carb Wonder
Shirataki noodles are a godsend for those following a carbohydrate-restricted diet. Containing less than 1 gram of carbohydrates per serving, they are primarily made from glucomannan, a soluble fiber derived from the konjac root. This makes them an excellent choice for blood sugar management.
Benefits of Glucomannan
Research indicates that glucomannan can significantly lower post-meal blood glucose levels, an essential factor in diabetes management. Additionally, it has been linked to weight loss and cholesterol improvement, both advantageous for those managing diabetes.
Versatile in Culinary Use
Shirataki noodles’ versatility is a key benefit, lending themselves to a variety of dishes from Asian stir-fries to Italian-inspired recipes. They serve as a perfect pasta substitute for those looking to control their carbohydrate intake, offering a strategic step towards better blood sugar control.
10. Tempeh: The Fermented Delight
Tempeh, a fermented soy product, is a nutritional gem, especially for those managing diabetes. A 100-gram serving of tempeh offers about 19 grams of protein and is rich in dietary fiber. This combination of high protein and fiber is beneficial for blood sugar control.

The Fermentation Factor
The fermentation process that tempeh undergoes not only enhances its digestibility but also introduces beneficial probiotics into the diet. These probiotics can improve gut health, which is increasingly recognized as important in diabetes management.
Low Glycemic Impact
With a Glycemic Index of just 15, tempeh is an excellent choice for maintaining stable blood sugar levels. Its low GI ensures a minimal impact on blood sugar, making it a safe and nutritious option.
Culinary Versatility
Tempeh is incredibly versatile and can be easily integrated into various dishes. It can be added to stir-fries, used in sandwiches, or even grilled as a meat alternative, making it a valuable addition to any diabetic-friendly meal plan.

9. Kimchi: The Spicy Probiotic Treat
Kimchi, the spicy and tangy Korean staple, is more than just a flavorful condiment. It’s low in calories, with about 30 calories per 100-gram serving, and packed with vitamins A and C.
Probiotics and Insulin Resistance
The probiotics found in kimchi, such as Lactobacillus, are essential for improving gut health and may play a role in enhancing insulin resistance, a key factor in diabetes management. These beneficial bacteria are a result of the fermentation process.
Antioxidants and Inflammation
Kimchi’s fermentation also enhances its antioxidant content. These antioxidants help combat inflammation, which is particularly beneficial for individuals with diabetes.
Adding Flavor and Health Benefits
Incorporating kimchi into your diet can add both flavor and health benefits. It can be eaten as a side dish, added to soups, or used in various recipes to provide a probiotic boost and aid in blood sugar regulation.
8. Quinoa: The Versatile Grain
Quinoa, a gluten-free grain, is unique in that it’s a complete protein, containing all nine essential amino acids. A cooked cup of quinoa provides about 8 grams of protein and nearly 5 grams of fiber, making it a valuable ally in blood sugar regulation.

Moderate Glycemic Index
Quinoa has a moderate Glycemic Index of around 53, making it a smart choice for those monitoring their blood sugar levels. This moderate GI contributes to a steadier blood sugar response.
Magnesium for Insulin Sensitivity
Quinoa is also loaded with magnesium, a mineral that plays a key role in improving insulin sensitivity. This is particularly important for individuals managing diabetes.
Culinary Uses
Quinoa’s nutty flavor and fluffy texture make it an excellent base for hearty salads, a wholesome side dish, or a nutritious breakfast alternative. Its versatility in recipes makes it easy to incorporate into a diabetic-friendly diet.

7. Walnuts: The Brain-Boosting Snack
Walnuts stand out for their high content of omega-3 fatty acids, especially alpha-linolenic acid, known for its anti-inflammatory properties. This makes them not just a brain-boosting snack, but also a valuable ally in diabetes management.
Fiber Content and Blood Sugar Control
A 30-gram serving of walnuts provides about 2 grams of fiber, which aids in the slower absorption of sugars and better blood sugar control. Regular consumption of walnuts has been linked to improved insulin resistance, making them a key addition to a diabetic diet.
Versatile and Delicious
Walnuts can be added to morning oatmeal, mixed into salads, or simply eaten as a snack. Their rich, nutty flavor and satisfying crunch make them a delightful addition to various dishes.
6. Blueberries: Nature’s Candy
Blueberries are celebrated for their health benefits, particularly in diabetes management. A study at the Pennington Biomedical Research Center showed a 22% improvement in insulin sensitivity in obese, insulin-resistant participants who consumed blueberry smoothies twice daily for six weeks.

Anthocyanins and Glycemic Control
The high anthocyanin content in blueberries, powerful antioxidants, plays a significant role in enhancing insulin sensitivity. With their low glycemic index and high fiber content, blueberries are ideal for managing blood sugar levels.
Enjoying Blueberries
Blueberries can be tossed into a morning yogurt, blended into smoothies, or enjoyed on their own. Their natural sweetness and nutritional profile make them a top choice for a diabetic-friendly diet.

5. Black Coffee with Cinnamon: The Zero-Sugar Kick
Black coffee, particularly when consumed without added sugars, has minimal impact on blood sugar levels. It’s a popular choice for a morning beverage that doesn’t spike glucose levels.
Cinnamon’s Blood Sugar Benefits
Adding cinnamon to coffee amplifies its health benefits. Cinnamon contains compounds that mimic insulin and improve blood sugar uptake. Consuming as little as half a teaspoon per day can significantly reduce fasting blood sugar levels.
A Simple, Health-Boosting Addition
Sprinkling cinnamon in your morning coffee is an easy, calorie-free way to enjoy a flavorful beverage while managing blood sugar levels. This combination is perfect for those monitoring their diabetes.
4. Wild Caught Salmon: The Omega-Rich Choice
Wild caught salmon is renowned for its high omega-3 fatty acid content, particularly EPA and DHA. These fats are crucial in reducing systemic inflammation, often an issue in diabetes, and can help alleviate insulin resistance.
Nutrient-Rich for Diabetes Management
A 3-ounce serving of wild salmon provides over 1,500 milligrams of essential omega-3s, along with vitamin D and selenium. These nutrients are important for glucose metabolism and immune function, playing a key role in diabetes management.
Improved Insulin Sensitivity
Studies suggest that regular consumption of omega-3 rich fish like salmon can improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes. Salmon’s high-quality protein content also helps stabilize blood sugar levels.
Culinary Versatility
Salmon can be grilled, baked, or poached, making it a versatile and delicious component of a diabetes-friendly diet. It’s a healthier alternative to high-saturated-fat meats, offering both flavor and health benefits.
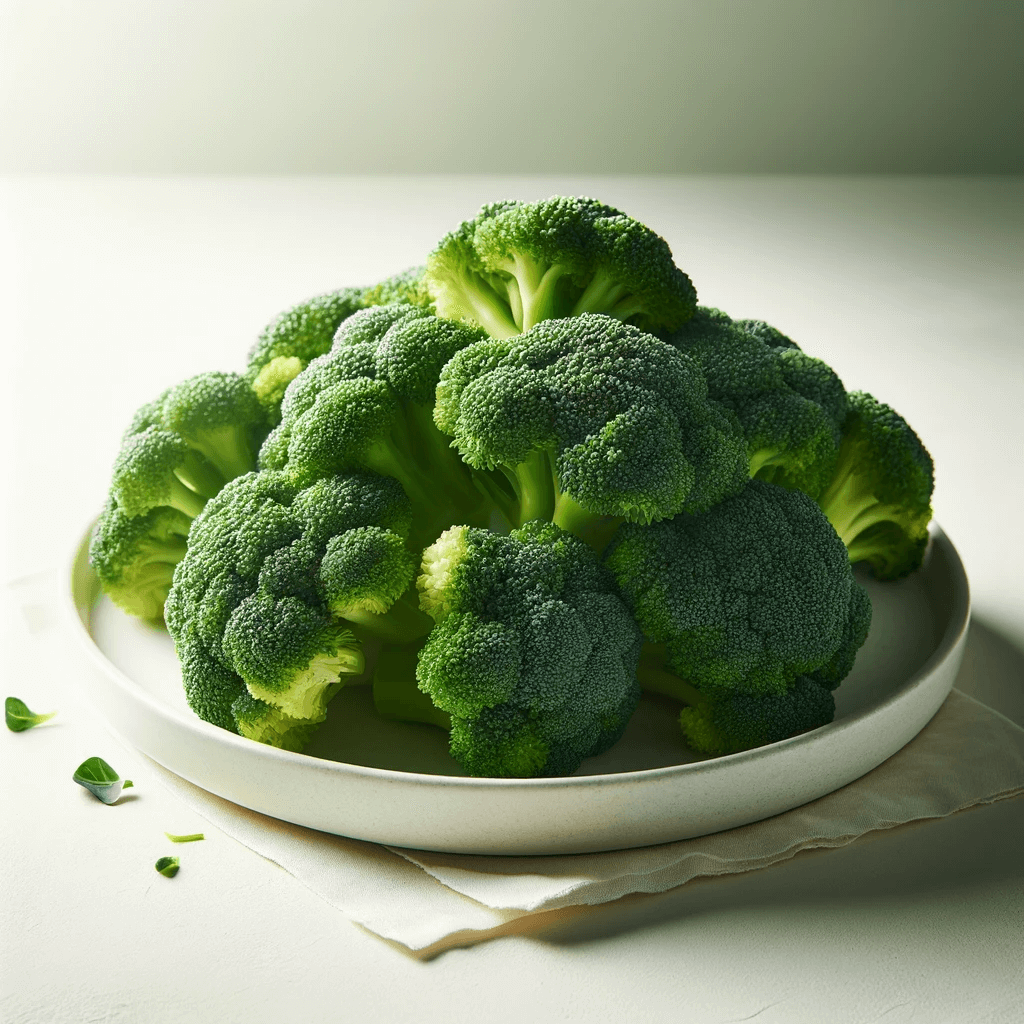

3. Broccoli: The Green Superhero
Broccoli, a cruciferous vegetable, is a powerhouse in diabetes management. Rich in fiber, antioxidants, and chromium, it excels in stabilizing blood sugar levels and enhancing insulin action.
Fiber and Glucose Absorption
A cup of cooked broccoli contains about 5 grams of dietary fiber, crucial for slowing glucose absorption. This helps in preventing sudden spikes in blood sugar levels, making broccoli an excellent choice for maintaining glycemic control.
Chromium and Insulin Efficiency
The chromium present in broccoli improves the metabolic action of insulin, enhancing its effectiveness. This mineral is key in managing blood sugar and improving overall metabolic health.
Sulforaphane: The Protective Compound
Broccoli is also rich in sulforaphane, a compound known to protect against cellular damage and improve blood sugar control. This makes broccoli not just a nutritious addition but also a strategic choice for a diabetes-friendly diet.
Versatile in Cooking
Broccoli can be steamed, roasted, or added to various dishes. Its versatility and nutritional profile make it an ideal vegetable for anyone looking to manage diabetes through diet.
2. Bone Broth: The Healing Elixir
Bone broth is rich in amino acids like glycine and proline. These amino acids are essential for repairing the gut lining and reducing inflammation, a common complication in diabetes that can exacerbate insulin resistance.
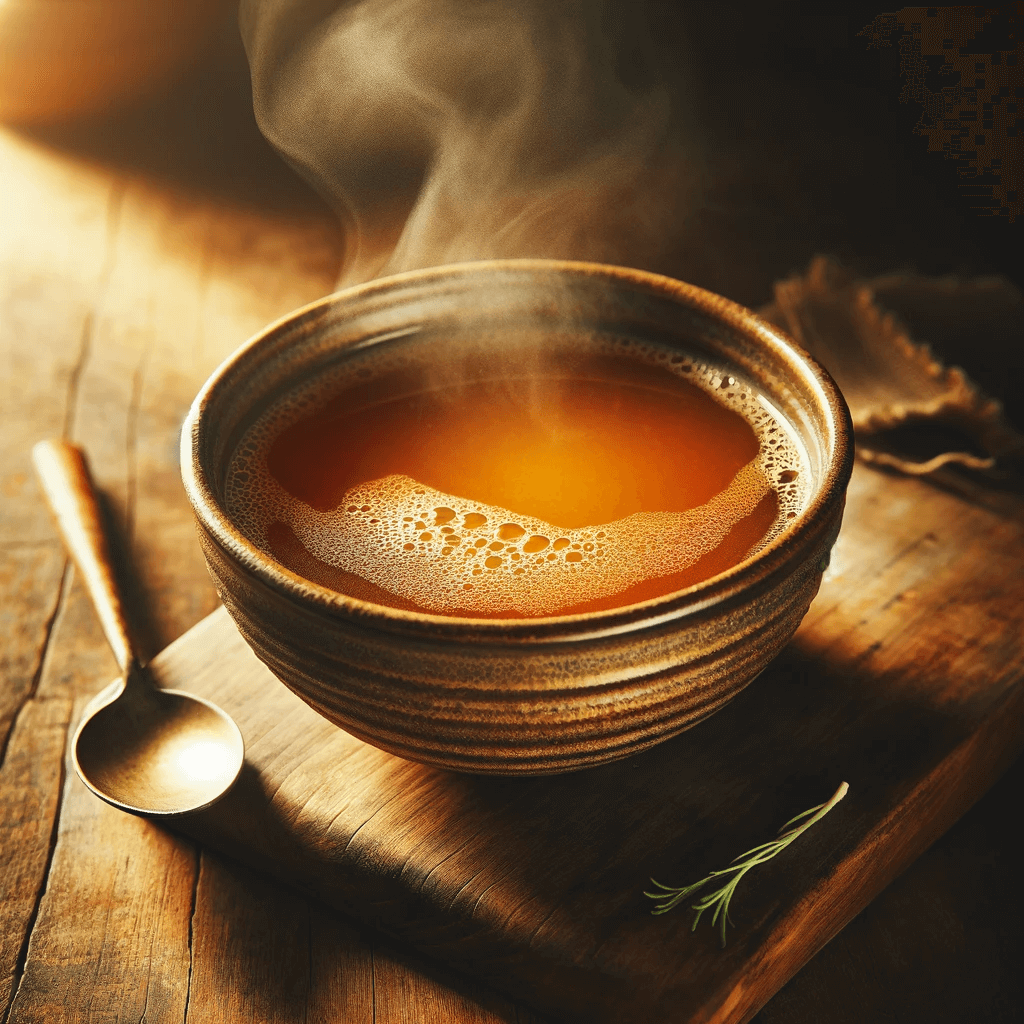

Minerals for Metabolic Function
Packed with minerals like calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus, bone broth supports bone health and various metabolic functions. This makes it not just beneficial for diabetes but also for overall health and well-being.
Collagen and Glucose Metabolism
The collagen in bone broth aids in healing the gut lining, which is crucial for optimal glucose metabolism and immune function. Regular consumption can lead to better glycemic control by supporting gut health and reducing inflammation.
Easy to Incorporate
Bone broth can be consumed on its own or used as a base for soups and stews. Its rich flavor and health benefits make it a valuable addition to a diabetes management plan.
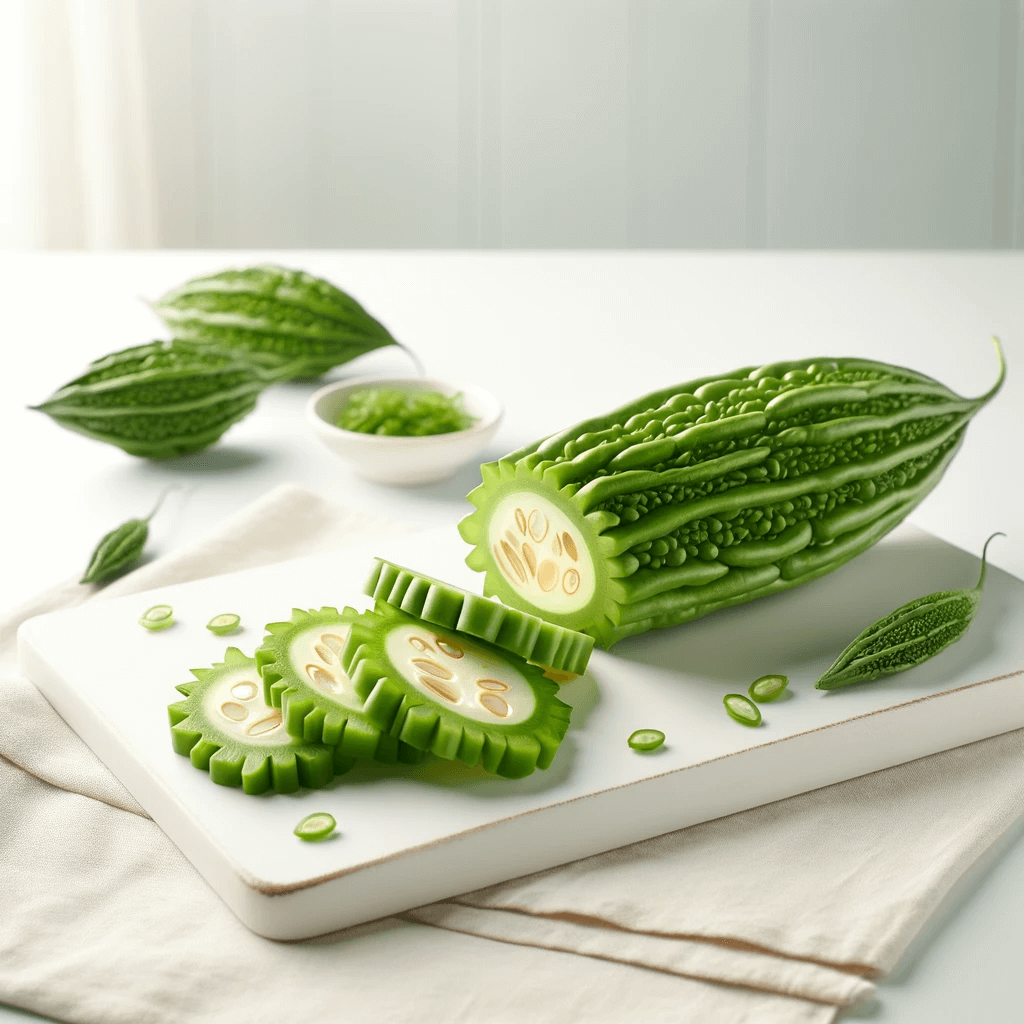

1. Bitter Melon: The Unexpected Champion
Bitter Melon is unique for its compounds like charantin, vicine, and polypeptide-p, which have insulin-like effects. These compounds help in lowering blood sugar levels, making bitter melon a potent food for diabetes management.
Clinical Evidence of Effectiveness
A study involving 100 participants with Type 2 diabetes found that consuming 2000 mg of bitter melon daily led to a significant reduction in blood sugar levels. This highlights its potential as a natural adjunct therapy for diabetes.
Nutritional Benefits
Rich in vitamins A and C, iron, and potassium, bitter melon contributes to overall health benefits. Its low-calorie yet high-fiber content makes it ideal for weight management, a crucial aspect of controlling Type 2 diabetes.
Culinary Uses
Bitter melon can be consumed in various forms, such as juices, extracts, or cooked as part of a meal. Its distinctive bitter flavor may require some adjustment, but its health benefits, particularly for diabetes management, are well worth it.
Empowering Your Diabetes Journey: Watch Our Informative Video
As we conclude our exploration of the top 13 anti-diabetic foods, it’s clear that managing diabetes goes beyond medication—it’s about making informed dietary choices. Each food item we’ve discussed offers unique benefits, from stabilizing blood sugar levels to reducing inflammation, all while adding delicious variety to your meals.
Remember, integrating these foods into your diet is a step towards taking control of your diabetes, not just a dietary change. To further aid in your journey, I encourage you to watch our detailed video on diabetes management through diet. This video will provide you with additional insights, practical tips, and visual guides to help you incorporate these foods into your daily routine effectively.
Watch the video now and take another step forward in your journey towards better health and diabetes control. Together, let’s transform the way we see and manage diabetes.





