Diabetes is a serious and chronic disease that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the body is unable to produce enough insulin or properly use the insulin it does produce, leading to high blood sugar levels. While diabetes affects various parts of the body, your feet can actually act as an early warning system for this condition. In fact, certain foot problems can be indicators of diabetes or its complications, highlighting the importance of taking care of the health of your feet. Recognizing these signs is crucial for early detection and proper management of the disease. In this blog post, we will explore 11 scary signs of diabetes that your feet might be showing, as well as how to respond to these signs and prevent complications.
Recognizing the Early Signs of Diabetes Through Your Feet
Diabetes can have a significant impact on foot health, and recognizing the early signs of the disease through your feet is essential. High blood sugar levels can cause nerve damage, known as diabetic neuropathy, which can lead to numbness, tingling, or pain in the feet. Additionally, diabetes affects blood flow, resulting in poor circulation to the extremities. Proper foot care, such as regular washing, drying, and moisturizing, can help prevent foot problems associated with diabetes, including the most common type of neuropathy, peripheral symmetrical neuropathy.
The Link Between Diabetes and Foot Health
There is a strong link between diabetes and foot health, primarily due to complications associated with diabetic neuropathy. Diabetic neuropathy is a type of nerve damage that can affect various parts of the body, including the feet. When high blood sugar levels persist, they can damage the small blood vessels that supply nerves, particularly those in the feet. This damage impairs nerve function, leading to numbness, tingling, or even loss of sensation in the feet. As a result, foot problems, such as sores, ulcers, infections, and foot deformities, can occur. These complications can be severe, potentially leading to amputation if left untreated.
Why Feet Are an Early Warning System for Diabetes
Your feet can serve as an early warning system for diabetes, indicating that something is amiss with your blood sugar levels and overall health. Changes in blood flow, which are common in diabetes, can affect your feet first due to their distance from the heart. The high blood sugar levels associated with diabetes damage blood vessels, contributing to poor circulation. This compromised blood flow can cause cold feet, slow wound healing, and increased risk of infections. Proper foot care, including regular self-examinations, wearing proper footwear, and maintaining good blood sugar control, is vital for preventing complications associated with diabetic foot problems. Don’t forget to check the bottoms of your feet for any changes or injuries that may require attention.
Detailed Look into the 11 Scary Signs of Diabetes Your Feet Might Show
Now, let’s take an in-depth look at the 11 scary signs of diabetes that your feet might show. While these signs can be alarming, they serve as valuable indications of the disease and its complications. By recognizing these signs, you can take proactive steps to manage your diabetes and prevent serious foot problems.
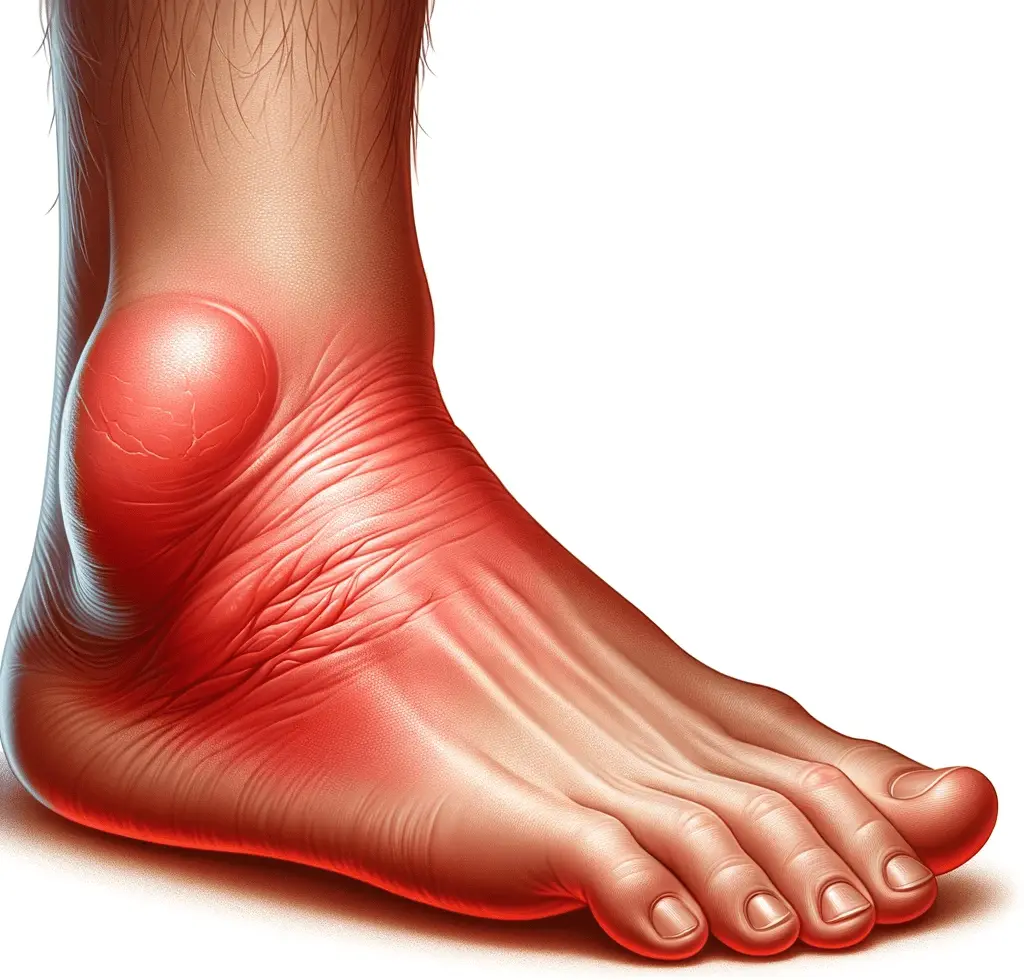
11. Swelling and Redness: What Does It Indicate?
Swelling and redness in the feet can be early signs of diabetic neuropathy and poor blood flow. When blood vessels are affected by high blood sugar levels, it can lead to fluid retention, causing swelling in the feet. Additionally, poor circulation can result in inadequate oxygen and nutrient supply, leading to redness. If you notice persistent swelling or redness in your feet, it is crucial to seek medical attention. These signs may indicate complications of diabetes, such as nerve damage, poor blood flow, or infection, and prompt treatment is necessary to prevent further problems.
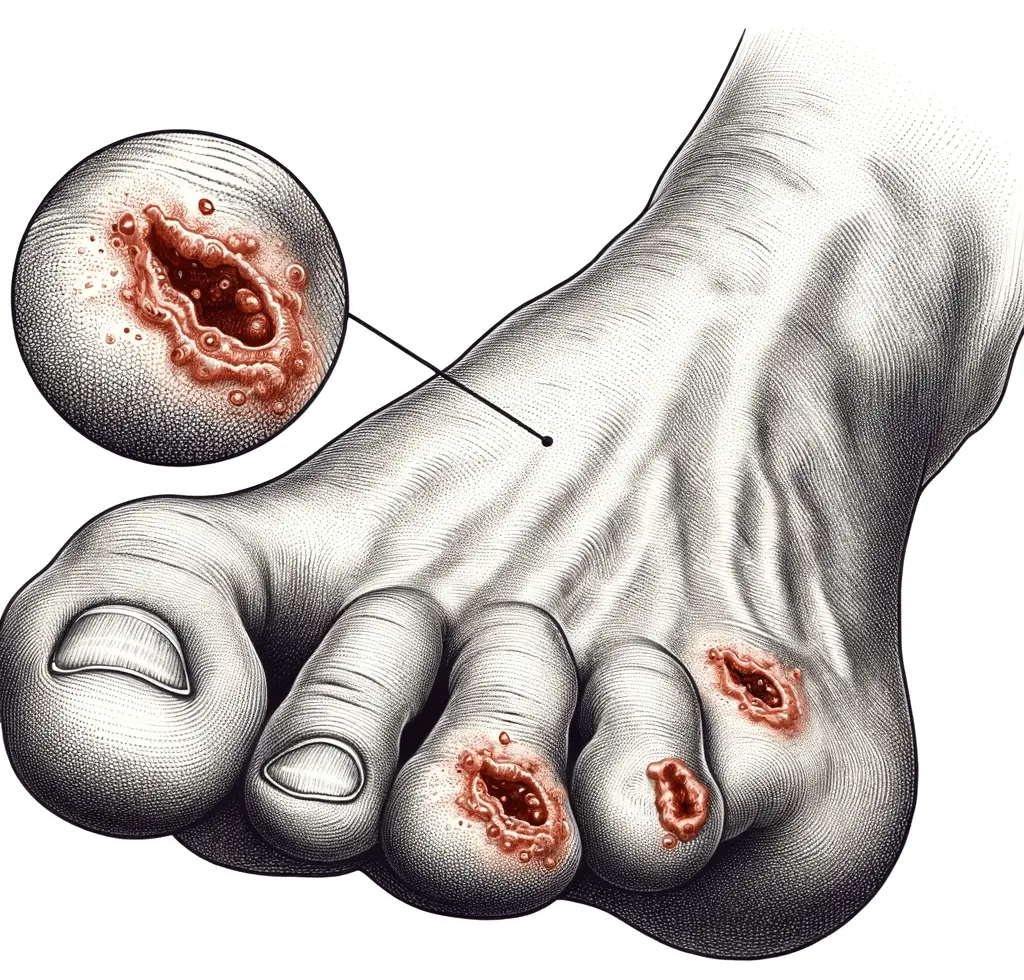
10. The Danger of Persistent Sores or Ulcers
Persistent foot sores or ulcers can be indicative of severe diabetic neuropathy and poor blood flow. When nerve damage and poor circulation are present, even minor cuts, scrapes, or blisters on the feet can become serious problems. High blood sugar levels can impair the healing process, making it difficult for these wounds to heal, leading to foot ulcers. Additionally, poor blood flow limits the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the affected area, further hindering the healing process. If you have persistent foot sores or ulcers, it is essential to seek immediate medical attention to prevent complications, including infections that could lead to amputation.
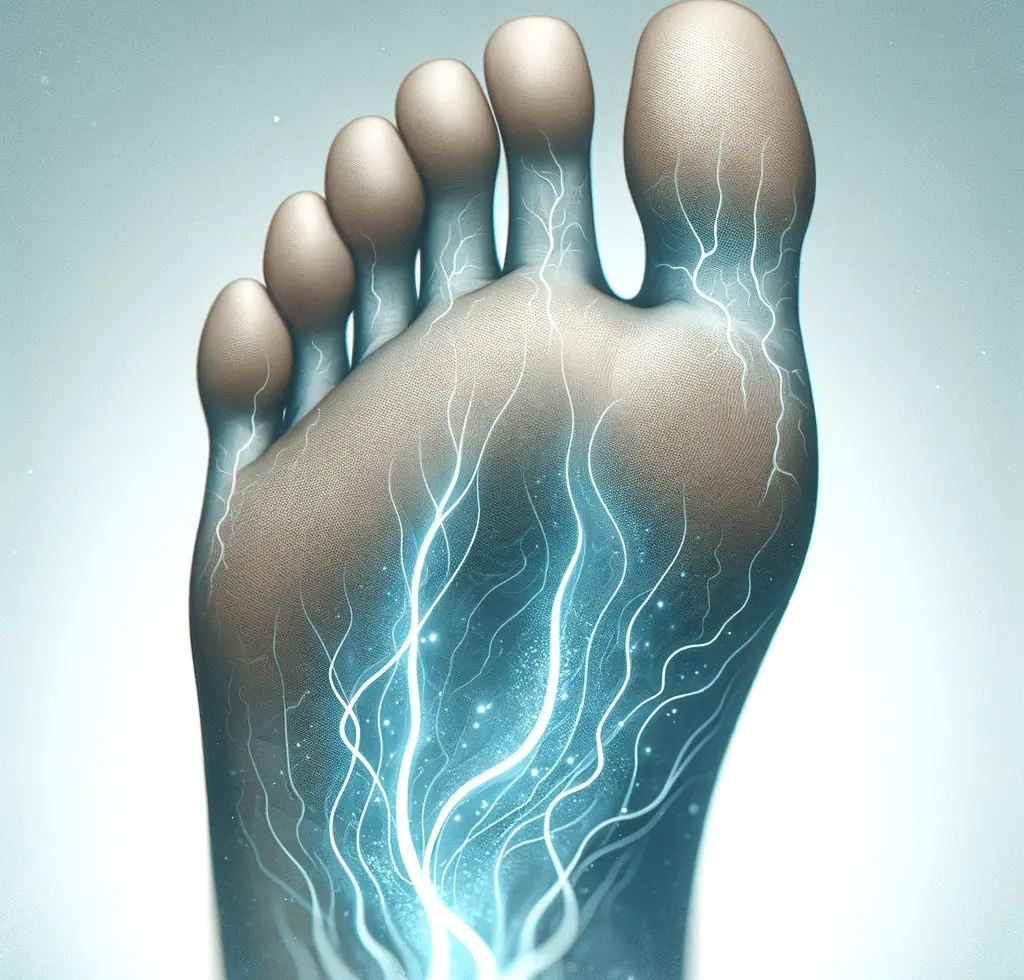
9. Numbness or Tingling Sensation: A Silent Alarm
Numbness or a tingling sensation in the feet is a common symptom of peripheral neuropathy, which is often associated with diabetes. The high blood sugar levels in diabetes can damage the peripheral nerves, leading to nerve damage and decreased sensation in the feet. This numbness can make it difficult to detect injuries or problems, increasing the risk of complications. If you experience numbness or tingling in your feet, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional as it may be a sign of diabetic neuropathy. Prompt diagnosis and management of this condition can help prevent further nerve damage and foot problems.
8. Changes in Skin Color: A Subtle Indicator
Changes in skin color, such as redness or paleness, can be subtle indicators of diabetic foot problems. When nerve damage and poor blood flow are present, it can affect the appearance of the skin on your feet. Reduced blood flow results in pale, cool skin, while poor circulation can also cause redness. It is crucial to monitor any changes in your foot’s skin color as they can indicate complications of diabetes, such as nerve damage, poor blood flow, or infection. Seeking medical attention for these changes is important to prevent further problems and promote foot health.
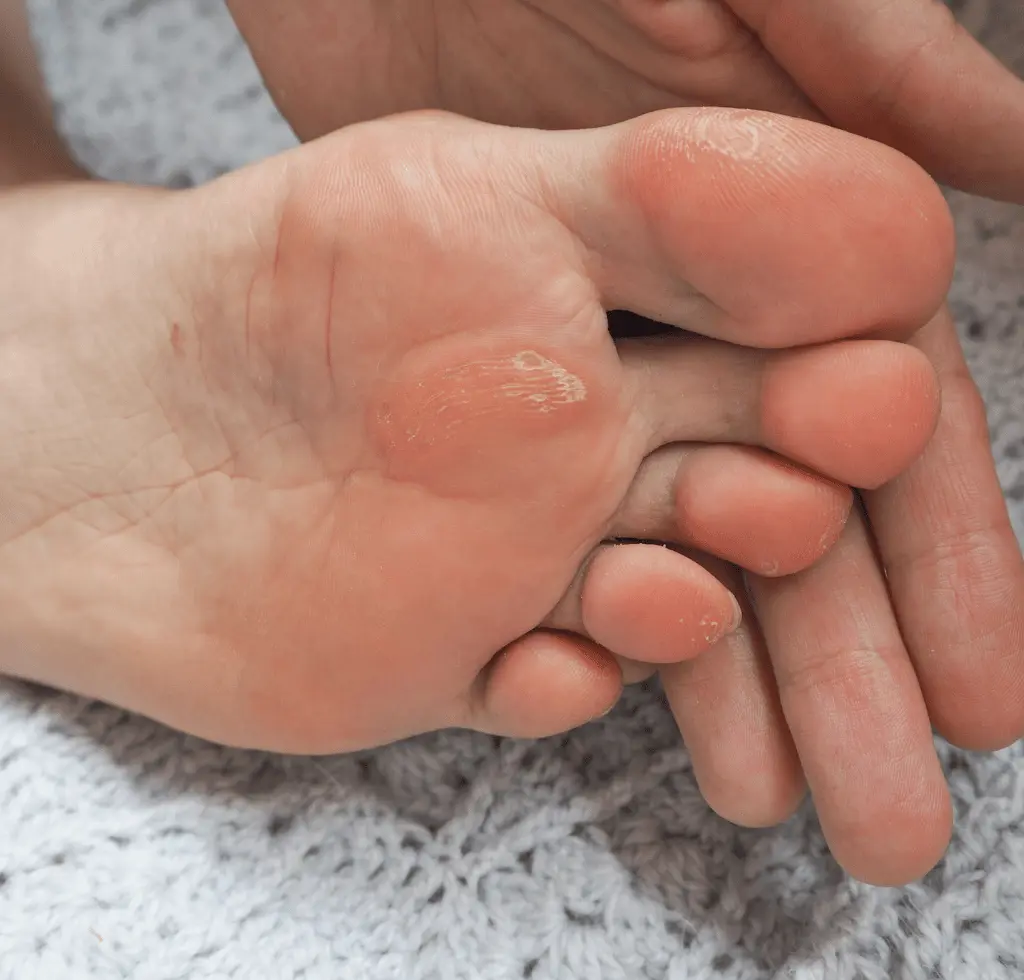
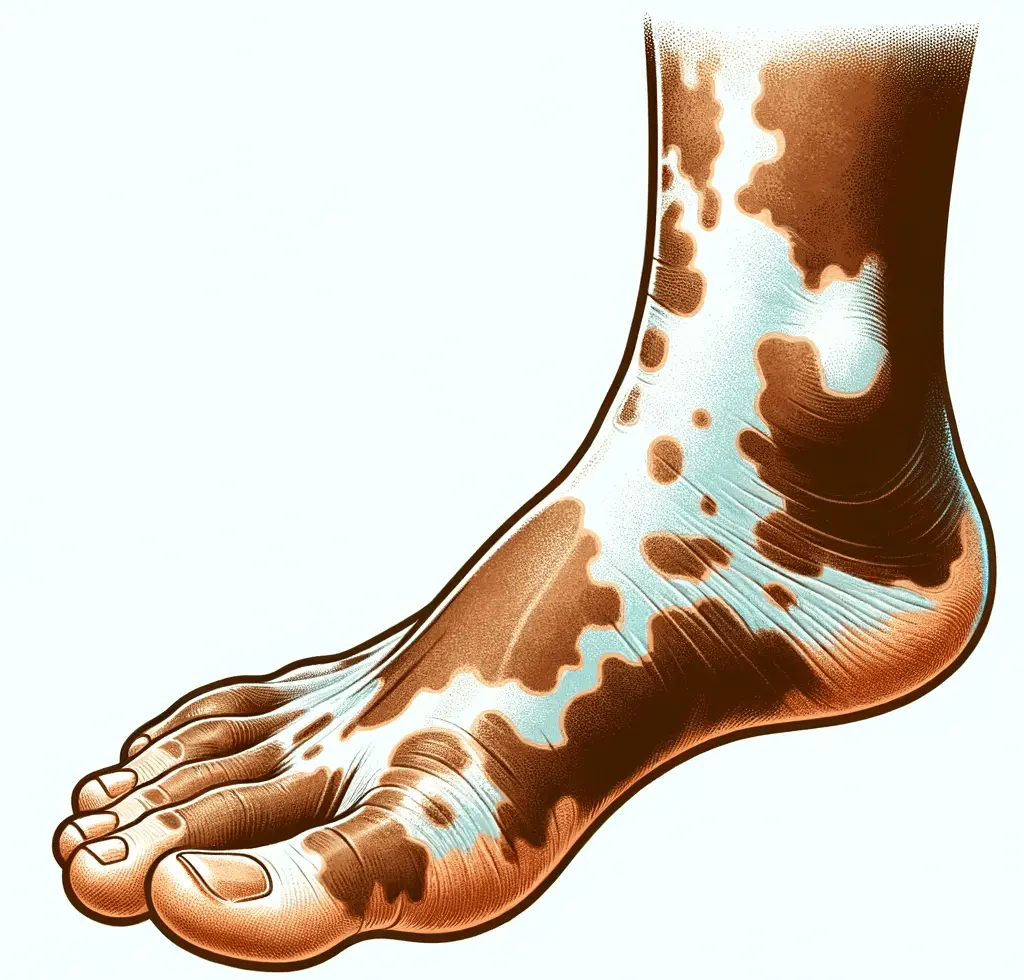

7. Fungal Infections: A Common Culprit
Fungal infections, such as athlete’s foot, are common foot problems that can affect diabetics. High blood sugar levels create an environment where fungi can thrive, increasing the risk of fungal infections. Additionally, nerve damage associated with diabetes can impair the body’s natural defenses against infections, making it harder to fight off fungal overgrowth. Proper foot care, including keeping feet clean and dry, wearing moisture-wicking socks and shoes, and avoiding walking barefoot or in ill-fitting shoes, such as slippers, is crucial in preventing and managing fungal infections in diabetics. If you suspect a fungal infection, it is important to seek prompt medical treatment to prevent complications and ensure proper healing.
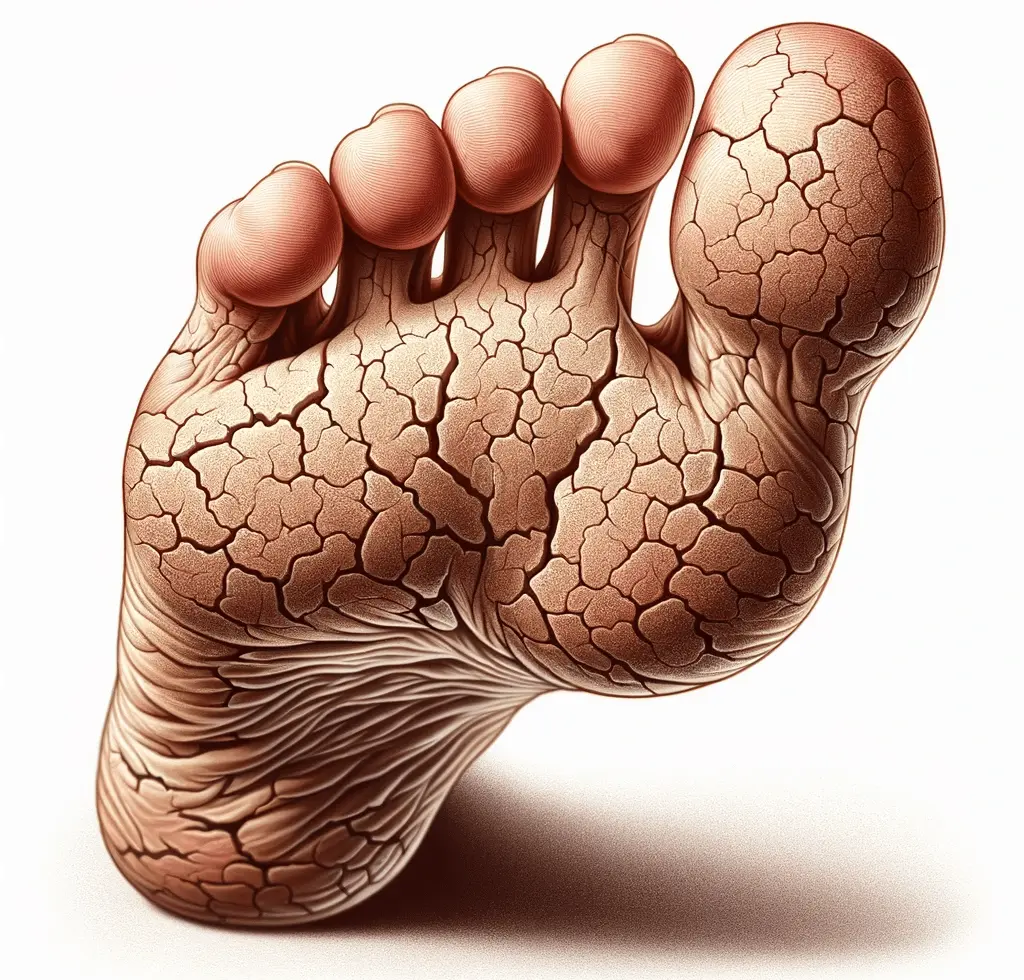
6. Understanding the Cause of Dry, Cracked Skin
Dry, cracked skin on the feet can be a sign of diabetic neuropathy, a type of nerve damage often associated with diabetes. Nerve damage impairs the body’s ability to produce adequate sweat and oil, leading to dryness. Additionally, high blood sugar levels can dehydrate the body, further contributing to dry skin. Diabetics should prioritize foot care, including regular moisturizing with lotion, wearing socks and shoes that allow proper airflow, and avoiding excessive foot soakings or exposure to extreme temperatures. Addressing dry, cracked skin promptly can help prevent complications, such as foot sores or infections, and promote overall foot health.
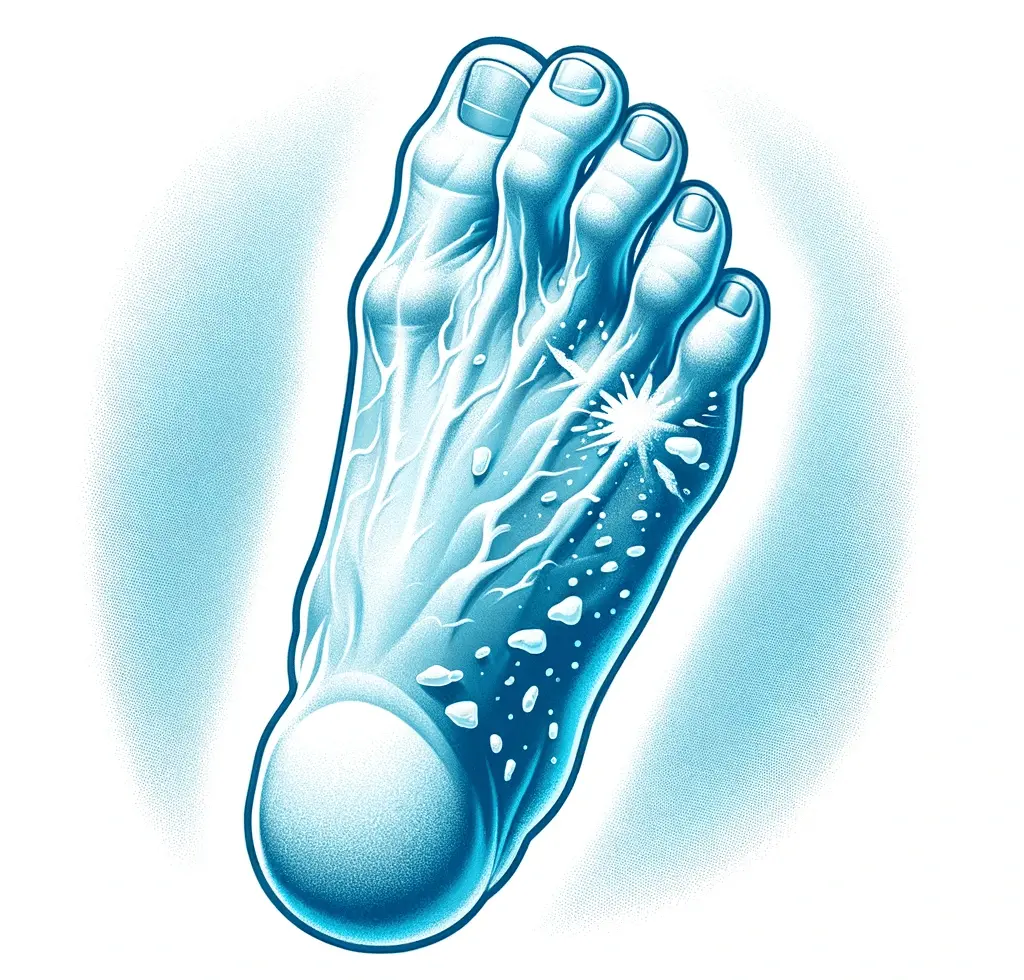
5. Cold Feet: More Than Just a Phrase
Having cold feet can be more than just a figure of speech; it might indicate poor blood flow, which is a symptom of diabetic neuropathy. Reduced blood flow to the feet can cause them to feel cold to the touch, and this condition is often associated with peripheral artery disease, another complication of diabetes. If you experience persistent cold feet, it is essential to seek medical attention. Proper blood flow is crucial for maintaining foot health, and addressing circulation problems can help prevent complications associated with poor blood flow and neuropathy.
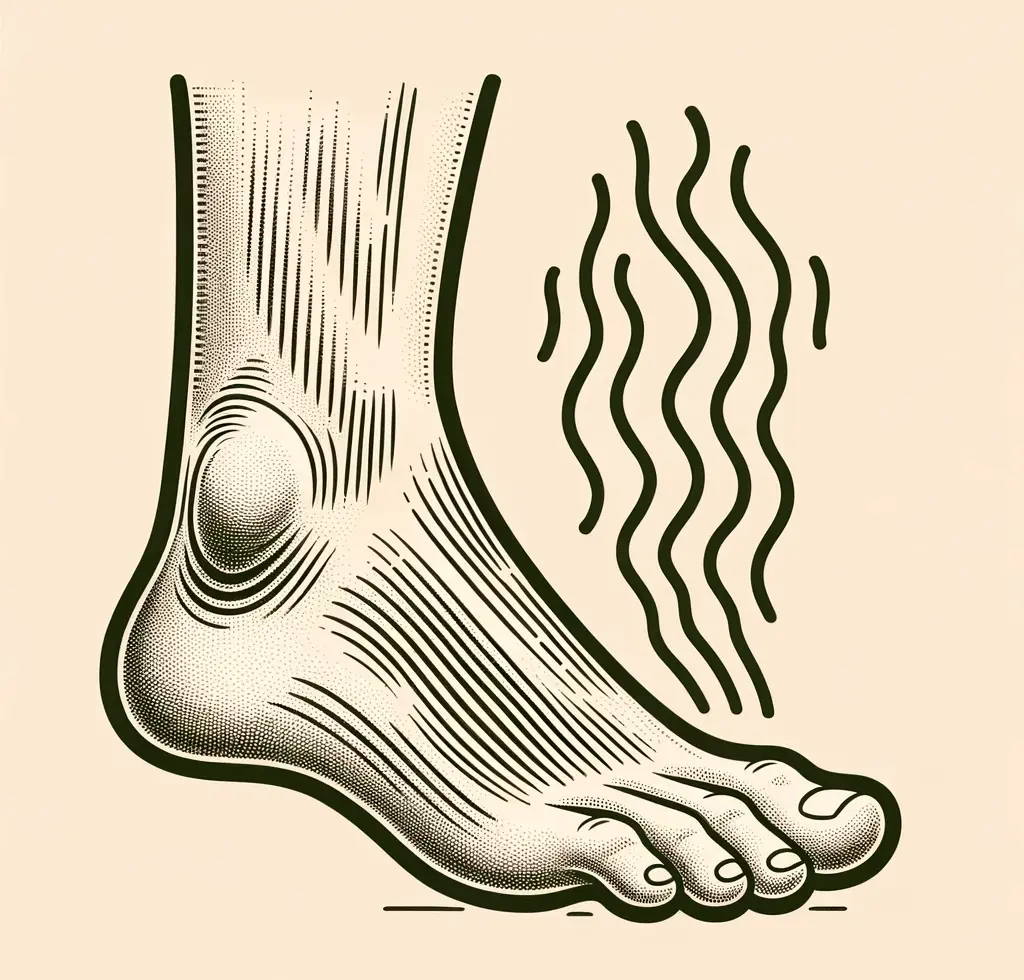
4. Unusual Foot Odor: An Unpleasant Warning Sign
Unusual foot odor can be a bothersome indication of diabetic foot problems. Diabetic neuropathy can affect the sweat glands in your feet, leading to changes in sweat production and resulting in an unpleasant foot odor. This change in sweat production can create an environment where bacteria and fungi thrive, leading to foot infections and other problems. If you notice a persistent, unusual foot odor, it is important to consult your health care provider. Proper foot hygiene, including regular washing, drying, and using foot powders, can help manage foot odor and prevent complications.
Deformities like Hammertoes or Bunions: Linked to Diabetes?
Diabetes can contribute to foot deformities, such as hammertoes and bunions, due to nerve damage. When nerve damage occurs, the muscles in the feet may lose their strength and elasticity, leading to imbalances and deformities. Hammertoes, where the toes curl or bend permanently, and bunions, which are bony bumps that develop at the base of the big toe, are common foot deformities associated with diabetes. Diabetics should prioritize foot care, including wearing properly fitting shoes, to prevent the development or worsening of these deformities. Early intervention and proper foot care play a crucial role in managing foot deformities associated with diabetes.
Sharp Pains or Cramps: A Red Flag
Experiencing sharp pains or cramps in the feet can be a red flag for diabetic neuropathy, nerve damage associated with diabetes. The high blood sugar levels in diabetes can damage the nerves, leading to abnormal sensations, including sharp pains or cramps. These sensations might occur spontaneously or trigger a physical response, such as scrunching your toes or rubbing your feet. If you experience sharp pains or cramps in your feet, it is important to seek medical advice. Managing blood sugar levels, maintaining foot health, and addressing nerve damage promptly can help prevent complications associated with diabetic neuropathy.
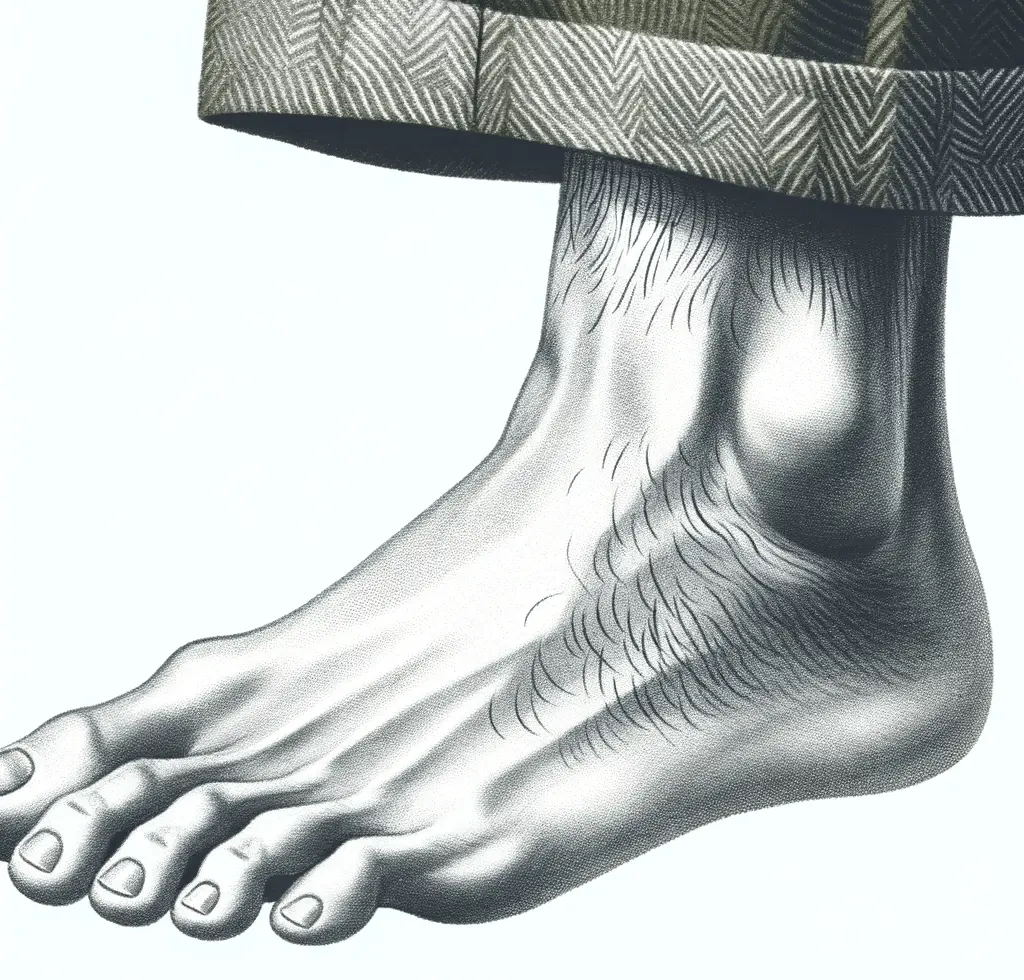
Loss of Hair on the Toes, Feet, and Lower Legs: A Surprising Symptom
A surprising symptom of diabetic neuropathy is the loss of hair on the toes, feet, and lower legs. Nerve damage associated with diabetes can disrupt proper blood flow to the hair follicles, leading to hair loss in these areas. This loss of hair might be gradual and affect large patches or be sparse and scattered. If you notice significant hair loss on your feet, it is important to consult your healthcare provider. Addressing any underlying nerve damage, such as autonomic neuropathy, improving blood flow, and managing blood sugar levels can help maintain foot health and potentially slow or prevent further hair loss.
How to Respond to These Signs
Recognizing the signs of diabetic foot problems can be alarming, but it is important to respond promptly to manage the disease effectively. If you notice any of these signs, it is crucial to take the following steps:
First Steps to Take When Noticing Symptoms
- Monitor your blood glucose levels: Keep track of your blood sugar levels regularly and notify your healthcare provider of any significant changes or consistent high levels.
- Seek medical attention: Make an appointment with your health care provider for a thorough foot examination if you notice any diabetic foot problems. They can provide a proper diagnosis, recommend treatment options, and offer guidance on foot care.
- Practice good foot care: Adopt a regular foot care routine, including washing and drying your feet daily, moisturizing your feet, practicing good toenail hygiene, wearing comfortable and supportive shoes, and avoiding walking barefoot.
Importance of Immediate Medical Attention
Immediate medical attention is vital upon noticing any signs of diabetic foot problems. Delaying medical care can result in serious complications, such as foot ulcers, infections, or amputation. By seeking prompt medical attention, you can receive appropriate treatment, including wound care, antibacterial agents, orthotics, or referrals to specialized foot care professionals. The earlier diabetic foot problems are detected and addressed, the better the chances of preventing severe complications and promoting foot health. Do not ignore the signs your feet are showing, as they can serve as crucial indicators of your overall diabetic health, especially if you have had high blood sugar levels for a long time.
Management and Prevention of Diabetic Foot Symptoms
Managing and preventing diabetic foot symptoms is crucial in maintaining foot health and reducing the risk of complications. By adopting a proactive approach, individuals with diabetes can take control of their foot health and minimize the impact of the disease.
Medical Interventions for Management
Medical interventions play a vital role in the management of diabetic foot symptoms. Here are some common interventions that your healthcare provider may recommend:
- Blood sugar control: Maintaining optimal blood sugar levels through diet, exercise, and appropriate medication is essential in delaying or preventing the progression of diabetic foot complications.
- Regular health care visits: Regular health care visits, including foot examinations, can help identify and manage any foot problems early.
- Treatment for diabetic neuropathy: Depending on the severity of diabetic neuropathy, your health care provider may prescribe medications to manage nerve pain, physical therapy to improve nerve function, or other specialized treatments.
Could Ignoring These Signs Lead to Severe Complications?
Ignoring the signs of diabetic foot problems could potentially lead to severe complications. When left untreated, diabetic foot complications can progress, putting individuals at risk of amputation, serious infections, foot ulcers, and even life-threatening conditions. Diabetic foot ulcers, caused by poor circulation, nerve damage, or pressure points, require immediate medical attention to prevent the development of infections. Untreated foot ulcers can deteriorate, leading to deeper, more severe wounds and potential amputation of a toe, foot, or part of your leg. Additionally, individuals with diabetic neuropathy may be more susceptible to a condition called Charcot foot, characterized by severe bone and joint damage due to significant nerve damage. Prompt diagnosis, treatment, and ongoing foot care are crucial in preventing severe complications associated with diabetic foot problems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it is crucial to pay attention to the signs that your feet might be showing, as they can indicate early symptoms of diabetes. From swelling and redness to persistent sores or ulcers, numbness or tingling sensation, changes in skin color, fungal infections, and more, these signs should not be ignored. Taking immediate action and seeking medical attention is essential to prevent further complications. By making lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy diet and exercising regularly, and considering medical interventions if necessary, you can effectively manage and prevent diabetic foot symptoms. Remember, ignoring these signs can lead to severe complications, so it is important to prioritize your foot health and overall well-being.