The Importance of Blood Sugar Management
If you think blood sugar management is only a concern for those with diabetes, it’s time to think again. The levels of sugar in your blood have far-reaching effects that permeate every corner of your body and affect how you feel, function, and even think. So let’s delve into why managing blood sugar is vital for not just diabetics but everyone.
Why Managing Blood Sugar is Crucial
Blood sugar, also known as glucose, is the primary source of energy for your body’s cells. Your body gets glucose from the food you eat and uses insulin, a hormone secreted by the pancreas, to shuttle glucose into cells where it can be used for energy. Sounds simple, right? But when this system is out of whack—due to factors like poor diet, lack of exercise, or stress—it can lead to fluctuating blood sugar levels, which is the gateway to a host of problems.
From Mood Swings to Medical Conditions
Imagine running out of fuel while driving; you wouldn’t get far, would you? Similarly, when your blood sugar drops, you may experience mood swings, fatigue, and a lack of focus. On the flip side, consistently high levels of blood sugar can set the stage for serious long-term health issues. We’re talking about heart diseases, kidney problems, and even the risk of stroke. So, the pendulum swings both ways—too low or too high is harmful.
Statistics on Diabetes
To put things in perspective, according to the World Health Organization, an estimated 422 million adults were living with diabetes in 2014, compared to 108 million in 1980. The global prevalence of diabetes among adults over 18 years of age rose from 4.7% in 1980 to 8.5% in 2014. These staggering numbers underline the importance of managing blood sugar effectively to prevent the onset of diabetes and its complications.
How Blood Sugar Affects the Body
Short-term Effects
- Mental Fog: Low or high blood sugar can affect your ability to concentrate, creating a mental fog that makes even simple tasks seem challenging.
- Energy Fluctuations: Ever felt that afternoon slump? Your blood sugar levels might be the culprit, as they can cause energy levels to rise and fall like a roller coaster.
- Mood Swings: Blood sugar imbalances can wreak havoc on your mood, making you go from jovial to irritable in the blink of an eye.
Long-term Effects
- Heart Disease: Chronic high blood sugar levels can lead to the development of heart diseases, including coronary artery disease.
- Kidney Failure: Over time, high levels of sugar can damage the intricate filtering system of the kidneys, leading to kidney disease or even failure.
- Nerve Damage: Elevated sugar levels can also cause damage to the nerves, particularly those in the feet, leading to conditions like neuropathy.
8. Regular Blood Sugar Checks
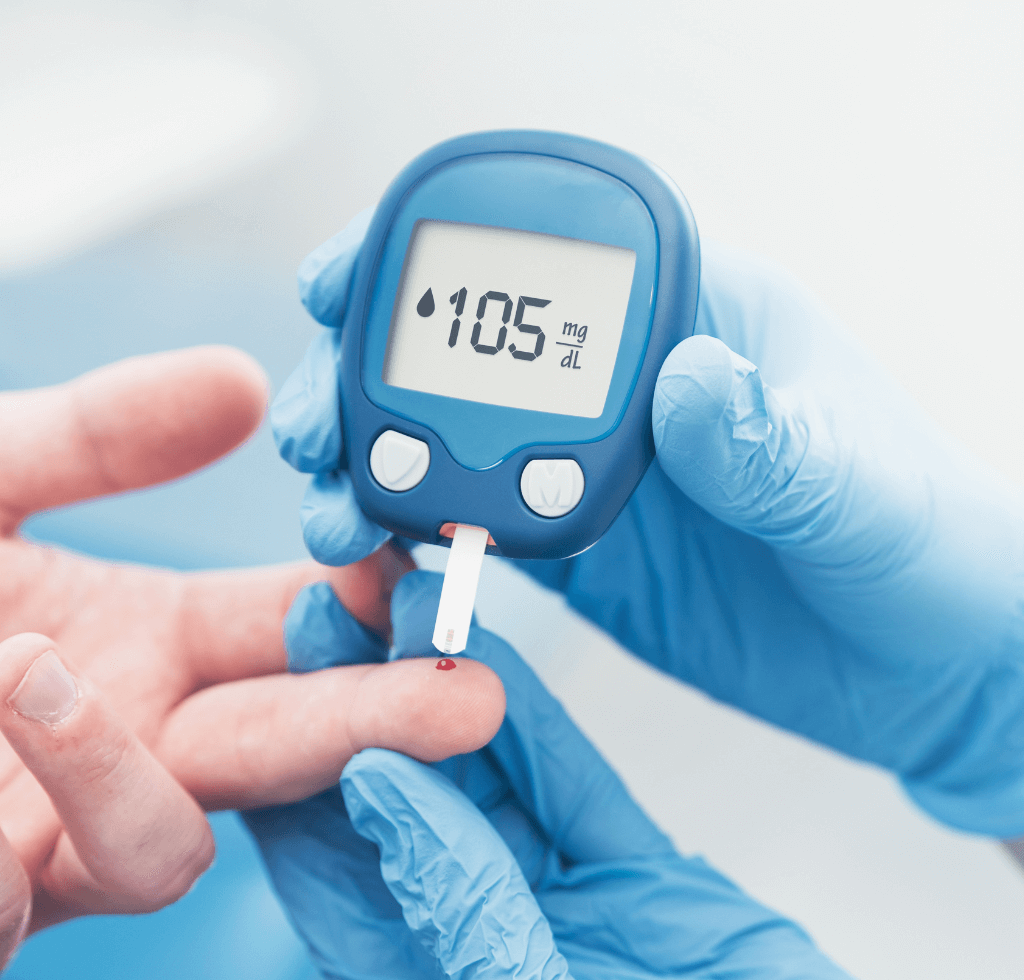
Now, diving in at number eight on our list is something so fundamental, yet often overlooked—Regular Blood Sugar Checks. Let’s not mince words here. You simply can’t manage what you’re not measuring.
Think about blood sugar monitoring as your health’s GPS; akin to how you wouldn’t traverse unknown streets without Google Maps guiding you, you shouldn’t navigate the labyrinthine world of health without a trusty glucose meter in hand.
The Science Behind Regular Checks
A compelling study published in the Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology underscores the importance of regular glucose monitoring. The research links consistent blood sugar checks with better glycemic control. Now, this isn’t some minuscule, marginal improvement. Regular checks serve as your real-time feedback loop. The sooner you know your levels, the faster you can take appropriate action—be it grabbing an apple or going for a brisk walk.
The Long-term Impact
If you’re pondering whether all this effort genuinely translates to significant gains, here’s some food for thought. According to the American Diabetes Association, diligent monitoring can not only maintain but actually improve your HbA1c levels. We’re talking about a striking average improvement ranging from 0.25% to 1.0%. In the grand scheme of diabetes management, that’s huge.
Make It Routine
So, what’s the bottom line? Make glucose monitoring non-negotiable. Keep your glucose meter within arm’s reach, and integrate checking your blood sugar into your daily routine—as regular as brushing your teeth or combing your hair.
7. Regular Exercise
Moving on to tip number seven, we’re stepping away from the glucose meter and straight into the gym or perhaps the park—yes, we’re talking about Regular Exercise. The sheer volume of benefits that physical activity offers to people managing their blood sugar is practically innumerable.

The Incredible Science of Exercise and Insulin Sensitivity
According to a comprehensive review published in the journal Diabetologia, the wonders of regular exercise extend far beyond the realm of weight loss or muscle toning. For people with type 2 diabetes, consistent physical activity can amplify insulin sensitivity by a staggering 51%. And for those without diabetes? A jaw-dropping improvement of 85%. Just let that sink in for a moment.
Quantifiable Benefits
If you’re the kind who finds solace in numbers, here’s something that will pique your interest. The American Diabetes Association has crunched the numbers and found that a mere 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week—amounting to roughly 20 minutes a day—can lead to a 0.6% to 1.0% reduction in HbA1c levels.
Make Exercise Non-negotiable
So, if you thought exercise was merely a vanity project reserved for those looking to shed a few pounds or sport a six-pack, it’s time to reconsider. Exercise is an indispensable, non-negotiable component of effective diabetes management. Whether it’s rolling out a yoga mat in your living room or lacing up your running shoes for a jog around the neighborhood, make physical activity an integral part of your daily routine.
6. Avoiding Processed Foods

Alright, let’s shift gears to our sixth tip, where we delve into the world of nutrition with laser-like focus on avoiding processed foods. You might be contemplating, “Is processed food really that devilish?” Well, the evidence doesn’t lie.
A study published in the Public Health Nutrition journal drives the point home: high consumption of ultra-processed foods increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes by a considerable 28%. This isn’t a figure to be taken lightly.
The Culprits in Processed Foods
The hazards of processed foods go beyond just high sugar content. They are often laden with unhealthy fats and preservatives. And let’s not forget sodium. According to the American Heart Association, processed foods are responsible for a staggering 75% of dietary sodium intake. When you couple this with diabetes, you’re looking at a recipe for hypertensive disaster.
The Fiber Factor
Another downside of processed foods? They often lack fiber—a crucial element for stabilizing blood sugar. The absence of fiber in these foods means you’re missing out on a key ally in your blood sugar management efforts.
The Better Choice
The message is clear: next time you find yourself in a grocery store, make a conscious decision to avoid the processed food aisles. Go for whole, fresh foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Your body and your blood sugar will show their gratitude in the form of better health.
5. Fiber Intake
As we ascend to tip number five, we’re shining the spotlight on an unsung hero of nutrition—Fiber. Often dismissed as “grandma food,” fiber is, in reality, a dynamo when it comes to managing blood sugar levels.

The Power of Fiber Explained
A compelling meta-analysis published in the Journal of the American Board of Family Medicine found that fiber isn’t just good for keeping you regular; it’s a game-changer for blood sugar management. The study found that increased fiber intake led to notable improvements in blood sugar control for both type 1 and type 2 diabetics. To put it in numbers, a fiber-rich diet was linked to a 0.55% reduction in HbA1c levels.
How Fiber Works
So how does fiber pull off this miraculous feat? Think of fiber as a slow-release mechanism for sugar. When you consume fiber-rich foods, it slows down the rate at which sugar is absorbed into the bloodstream. This helps to flatten those dreaded spikes and troughs in blood sugar levels.
Incorporating Fiber into Your Diet
It’s easy to incorporate more fiber into your diet. Add an extra helping of leafy greens to your plate, snack on fruits like apples and pears, or include whole grains like oats and barley in your meals. It doesn’t take much to make a significant impact on your blood sugar management. Your body will surely thank you for that extra scoop of spinach or that apple you decided to eat as a snack.
4. Intermittent Fasting

At number four, we’re diving into a topic that’s been garnering a lot of attention lately—Intermittent Fasting. This isn’t just a fad or a trendy buzzword; there’s substantial scientific research supporting its effectiveness.
A study conducted in 2018, published in the journal Cell Metabolism, highlights the promise intermittent fasting holds for improving insulin sensitivity and, consequently, lowering blood sugar levels. The data indicate that fasting glucose levels can reduce by 3-6%, and fasting insulin levels can drop by a significant 20-31%. It’s akin to giving your body’s insulin function a refreshing, much-needed reboot.
The American Diabetes Association’s Stance
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) has also begun to acknowledge the potential upsides of intermittent fasting, stating that it can be a viable option for those who can manage it safely. This serves as a substantial nod from a reputable organization, underscoring the legitimacy of intermittent fasting as a blood sugar management strategy.
Different Methods of Intermittent Fasting
If you’re growing weary of the monotonous meal timing and are open to trying something new, intermittent fasting offers various methods to fit different lifestyles. The 16/8 method, which involves fasting for 16 hours and eating within an 8-hour window, is among the most popular. But remember, intermittent fasting isn’t a one-size-fits-all approach.
Consult Your Healthcare Provider
It’s crucial to consult your healthcare provider before implementing drastic changes like intermittent fasting, especially if you’re managing conditions like diabetes. Customized medical advice is vital for effective and safe blood sugar management.
3. Quality Sleep
As we move into the top three, let’s discuss an aspect often overlooked when it comes to blood sugar management—Quality Sleep. A study published in the Diabetes Care journal draws a direct line between poor sleep and reduced insulin sensitivity, by as much as 25%.

In layman’s terms, inadequate sleep can sabotage your efforts to control blood sugar, often without you even realizing it.
The Importance of Sleep Quantity and Quality
The general recommendation is a minimum of 7 hours of sleep per night for adults. However, it’s not just about the number of hours; the quality of sleep is equally crucial. Poor sleep quality can lead to elevated HbA1c levels, adding another layer of intricacy to effective blood sugar management.
The Connection Between Sleep and Food Choices
Have you ever noticed how you’re more likely to reach for sugary snacks or processed foods when you’re running on insufficient sleep? That’s not merely coincidental; it’s your sleep-deprived body playing tricks on you, nudging you towards choices that can spike your blood sugar levels.
Prioritize Sleep for Blood Sugar Control
In the grand scheme of things, focusing on sleep might be one of the simplest yet most impactful lifestyle adjustments you can make for better blood sugar control. Ensuring that you get sufficient, high-quality sleep can be a cornerstone in your overall strategy to manage blood sugar levels effectively.
2. Stress Reduction

Coming in at a significant second place on our list is something that’s easier said than done—Stress Reduction. You’ve likely heard the adage, “Stress is a silent killer,” and when it comes to blood sugar management, this couldn’t be more accurate.
A study published in the journal Psychoneuroendocrinology reveals a startling fact: stress hormones like cortisol can elevate blood glucose levels by a considerable margin—up to 23%. In essence, unmanaged stress can be like throwing a wrench into the well-oiled machinery of your diabetes management efforts.
The Widespread Impact of Stress
The American Psychological Association has reported that a whopping 43% of adults suffer adverse health effects due to stress. These effects aren’t just general health concerns; they can directly complicate the control of diabetes and blood sugar levels.
Techniques for Stress Reduction
So, what can you do when you’re caught in the storm of stress? There are several proven techniques that can help you navigate these choppy waters. Mindfulness practices, deep breathing exercises, and even physical activities like yoga or a quick jog can significantly mitigate stress levels.
Incorporate Stress Management into Your Routine
The next time you find yourself overwhelmed by stress, remember that your blood sugar levels are also at stake. Make it a point to incorporate stress management techniques into your daily routine. Whether it’s taking deep breaths during a busy workday or dedicating 10 minutes to mindfulness before bedtime, every little bit helps.
1. Consult a Healthcare Provider
Finally, the tip that tops them all—Consult a Healthcare Provider. While self-care and lifestyle changes are crucial, they can’t replace the nuanced guidance that only a qualified healthcare provider can offer.

A study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association drives this point home: patients who actively collaborate with their healthcare providers have a 19% lower risk of experiencing hyperglycemia and a 7% lower risk of hypoglycemia.
The Importance of Personalized Care Plans
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) stresses the value of personalized care plans for effective diabetes management. Remember, no two individuals with diabetes are identical; therefore, your management plan should be as unique as you are.
Beyond Medication
Consulting a healthcare provider isn’t just about getting a prescription for medication, although that’s often a vital component. It’s about a comprehensive approach to managing your diabetes. This includes dietary recommendations, exercise plans, and even mental well-being strategies tailored to improve your blood sugar control.
Take the Step to Consult
If you haven’t scheduled that all-important check-up yet, what’s holding you back? Your best path to stable blood sugar doesn’t just start in your kitchen or your local gym; it starts in your healthcare provider’s office.
Take Control, Lower Your Sugar
We’re nearing the end of this comprehensive guide, but remember, the journey to effective blood sugar management is ongoing. Whether it’s committing to regular exercise, making smarter dietary choices like increasing fiber intake and avoiding processed foods, or embracing scientifically-backed methods like intermittent fasting, the power to control your blood sugar lies in your hands. But it’s not just about lifestyle changes; consulting a healthcare provider and managing stress also play vital roles in this equation. These aren’t just tips; consider them essential practices backed by substantial scientific evidence, aimed at helping you lead a healthier, more balanced life. So don’t delay; your path to better blood sugar control starts now. It’s time to take control and lower your sugar for a life that’s not just longer, but richer in quality.
You’ve just read through 8 proven tips for quickly lowering your blood sugar. If you’re looking for a fast review or a quick guide to keep at your fingertips, check out the summary video below. It condenses all eight tips into a short, easy-to-follow format. A must-watch for anyone serious about immediate blood sugar control!
FAQs
1. How often should I check my blood sugar levels?
The frequency of blood sugar checks varies depending on individual circumstances, such as the type of diabetes you have and your current treatment plan. It’s crucial to consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice. Generally, people with type 1 diabetes may need to check more frequently than those with type 2 diabetes.
2. Can exercise really improve my insulin sensitivity?
Absolutely, regular exercise has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity significantly. Studies indicate that even 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week can lead to measurable improvements in blood sugar control.
3. Are processed foods really that bad for blood sugar?
Yes, processed foods often contain high levels of sugar, unhealthy fats, and sodium, which can negatively impact your blood sugar levels. They also usually lack fiber, an essential nutrient for stabilizing blood sugar.
4. What are some effective stress-reducing techniques?
Mindfulness, deep breathing exercises, and physical activity like yoga or jogging can be highly effective in reducing stress. Even dedicating just 10 minutes a day to stress-reducing activities can make a notable difference.
5. Is intermittent fasting safe for everyone?
Intermittent fasting can be effective for improving blood sugar control, but it’s not suitable for everyone. Certain groups, like pregnant women, children, and individuals with certain medical conditions, should avoid it. Always consult your healthcare provider before beginning any new diet regimen, especially one that involves fasting.





